The Beginner’s Guide to Vector Databases: Understanding the Basics
As technology advances, so does the way we handle data. Traditional databases are great for numbers and straightforward data, but they fall short when it comes to more complex stuff like images, videos, and large text files. That’s where vector databases come in, providing a smart solution for today’s data challenges. Let’s break down what vector databases are, their pros and cons, what they’re used for, and how to choose the right one for your needs.
What is a Vector Database?
Imagine if you could search for data not by exact match, but by similarity. That’s what vector databases do. They store information as vectors—basically, long lists of numbers that a computer uses to understand and compare different pieces of data. This makes it super easy to find things that are similar to each other, even in a huge sea of information.
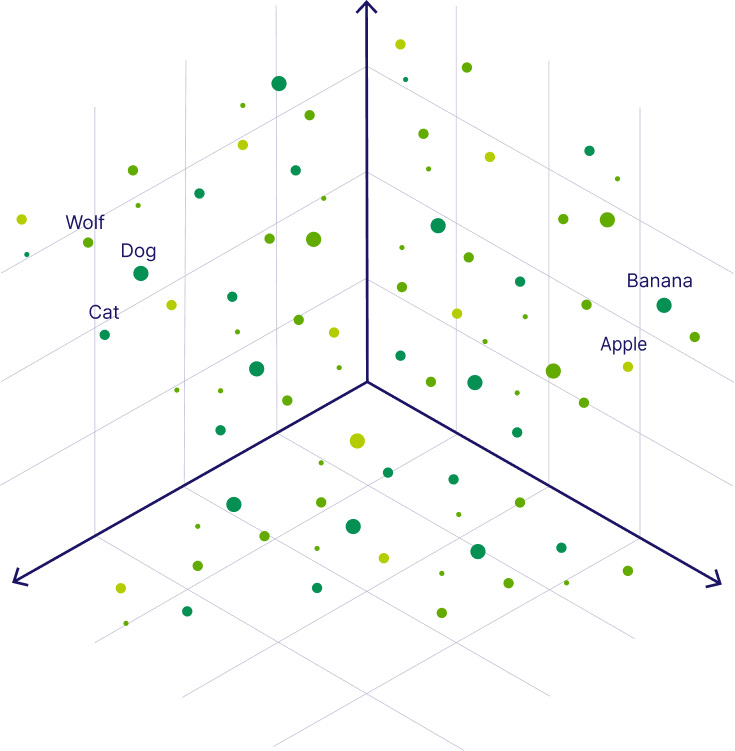
Illustration of a 3D vector space where data points represent words grouped by similarity. For instance, ‘Wolf’, ‘Dog’, and ‘Cat’ are closer together in space, while ‘Apple’ and ‘Banana’ form a distinct cluster, demonstrating semantic relationships in a vector database.
Benefits of Vector Databases
1. Quick Searches for Similar Items: If you’ve ever used a website that suggests products or movies based on what you like, you’ve seen vector databases in action. They’re fantastic at quickly finding items that resemble each other.
2. Handles Lots of Data Easily: These databases are built to manage large amounts of data smoothly, which is perfect for businesses dealing with tons of information.
3. Works Well with AI: Vector databases fit nicely with AI and machine learning, making them a go-to for applications that use these technologies.
Downsides of Vector Databases
1. Complex to Manage: Setting up and maintaining these databases can be tricky unless you really know what you’re doing.
2. Requires Strong Hardware: They need powerful computers to run effectively, which can get expensive.
3. Limited in Flexibility: If you need to run complex queries or combine different types of data, vector databases might not be the best choice.
Popular Vector Databases
Here are some well-known vector databases:
• Pinecone: Known for its scalability and ease of use, Pinecone is a good choice for businesses that need robust, scalable vector search capabilities.
• Milvus: An open-source vector database that supports multiple similarity metrics and is designed for high performance in large-scale environments.
• Weaviate: An open-source vector search engine that integrates seamlessly with machine learning models and offers GraphQL and RESTful interfaces.
• Faiss by Facebook AI: Primarily a library for efficient similarity search, Faiss is often used in combination with databases to handle vector data effectively.
• Annoy by Spotify: Another library focused on nearest neighbor search, useful for building custom vector database solutions.
When to Use Vector Databases
1. Finding Similar Content: Whether it’s searching for similar images or recommending music based on what you already like, vector databases make these tasks a breeze.
2. Custom Recommendations: Online stores and streaming services use these databases to suggest products or shows you might enjoy.
3. Spotting Fraud: In banking, vector databases help spot unusual patterns that could indicate fraud.
4. Understanding Human Language: They help chatbots and search engines understand and respond to natural language more effectively.
For example, the idea of “King - Man + Woman = Queen” in language processing shows how these databases can understand relationships and similarities between words.
Choosing the Right Vector Database
Here’s what to consider:
1. Size and Growth of Your Data: Make sure the database can handle your current data and any increase in the future.
2. Speed Needs: Think about how fast you need the system to respond to queries.
3. Compatibility: Check whether the database works well with other systems you’re using.
4. Budget: Consider both the purchase cost and what you’ll spend on running the hardware.
Conclusion
Vector databases are changing the game for businesses that deal with complex, varied data types. By choosing the right database, you can enhance your applications with fast, relevant data retrieval, making your operations smoother and more efficient. Whether you’re recommending products, detecting fraud, or improving customer interactions, vector databases can provide the tools you need to succeed.